DESCRIPTION:
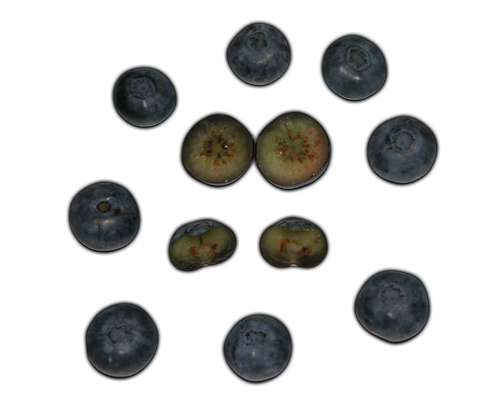
Blueberries are flowering plants of the genus Vaccinium (a genus which also includes cranberries and bilberries) with dark-blue berries. Species in the section Cyanococcus are the most common fruits sold as "blueberries" and are mainly native to North America. They are usually erect but sometimes prostrate shrubs varying in size from 10 centimetres (3.9 in) to 4 metres (160 in) tall. In commercial blueberry production, smaller species are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild") and the larger species, are known as "highbush blueberries". The leaves can be either deciduous or evergreen, ovate to lanceolate, and 1 - 8 centimetres (0.39 - 3.1 in) long and 0.5 - 3.5 centimetres (0.20 - 1.4 in) broad. The flowers are bell-shaped, white, pale pink or red, sometimes tinged greenish.
The fruit is a false berry 5 - 16 millimetres (0.20 - 0.63 in) diameter with a flared crown at the end; they are pale greenish at first, then reddish-purple, and finally blueish-purple when ripe. They have a sweet taste when mature, with variable acidity. Blueberry bushes typically bear fruit in the middle of the growing season: fruiting times are affected by local conditions such as altitude and latitude, so the height of the crop can vary from May to August depending upon these conditions.
Commercially offered "wild blueberries" are usually from species that naturally occur only in eastern and north-central North America. Other sections in the genus, native to other parts of the world including western North America, South America, Europe, and Asia, include other wild shrubs producing similar-looking edible berries such as huckleberries in (North America) and bilberries (Europe). These species are sometimes called "blueberries" and sold as blueberry jam or other products.
|